Revolutionizing Diagnosis with Machine Learning
The Challenge: Delayed Diagnosis in Critical Diseases
Early detection of diseases like pneumonia, cancer, and cardiovascular conditions significantly improves patient outcomes. However, traditional diagnostic methods rely heavily on manual analysis by radiologists, pathologists, and healthcare professionals, which can lead to:
- Delays in diagnosis due to increasing patient loads.
- Human error and variability in interpretation.
- Limited access to specialists in rural or underdeveloped regions.
To overcome these challenges, AI is now being integrated into medical imaging, predictive analytics, and diagnostic workflows to enhance accuracy and efficiency in healthcare.
How AI is Transforming Disease Detection
AI-driven diagnostic tools leverage deep learning, computer vision, and predictive modeling to assist doctors in identifying diseases with higher precision and speed.
1. AI-Powered Medical Imaging (Deep Learning for Diagnosis)
Medical imaging generates vast amounts of X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans, which AI models can analyze faster and often with greater accuracy than human experts.
How It Works:
- Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) analyze medical scans for patterns associated with diseases.
- AI models trained on millions of labeled images detect anomalies, tumors, and infections.
- Provides heatmaps and visual explanations for radiologists to validate findings.
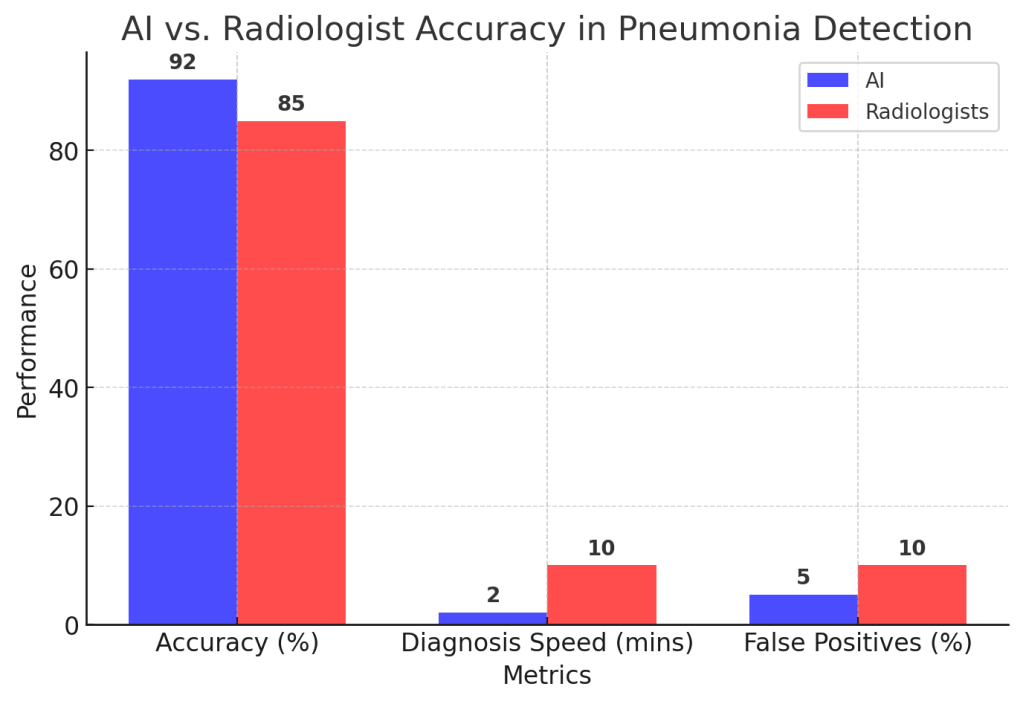
Example: Researchers at Stanford developed a CNN model for pneumonia detection, which achieved a 92% accuracy rate, outperforming human radiologists in identifying pneumonia from chest X-rays.
Graph: AI vs. Radiologist Accuracy in Pneumonia Detection
2. Predictive Analytics for Disease Risk Assessment
Machine learning models analyze patient data, including medical history, lifestyle factors, and genetic markers, to predict the likelihood of developing chronic diseases.
Key AI Techniques:
- Random Forest & Gradient Boosting – Identify risk factors for heart disease and diabetes.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) – Extract key insights from patient records and medical literature.
- Time Series Forecasting – Predict disease progression and recommend early interventions.
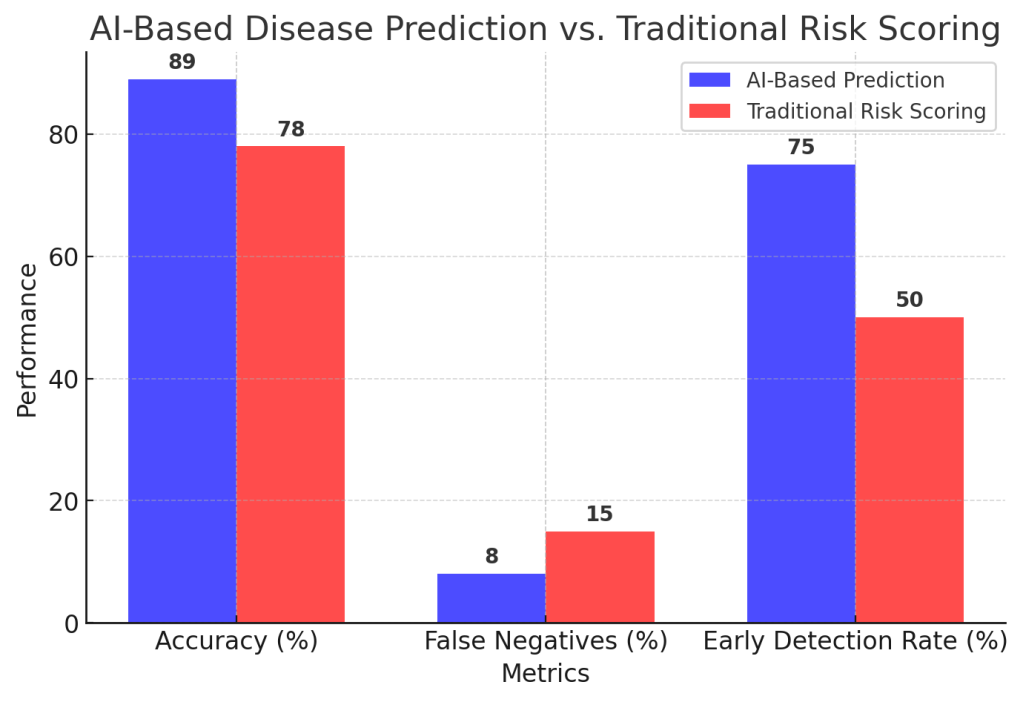
Example: The Mayo Clinic deployed an AI system that can predict sepsis risk in ICU patients hours before symptoms appear, reducing mortality rates by 20%.
Graph: AI-Based Disease Prediction vs. Traditional Risk Scoring
3. AI in Personalized Treatment Plans
AI-driven models help doctors develop customized treatment strategies based on a patient’s unique genetic profile, medical history, and response to previous treatments.
How AI Enhances Personalized Medicine:
- Genomic Data Analysis – AI processes DNA sequencing data to tailor cancer treatments.
- Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS) – Recommends personalized drug regimens based on real-world patient outcomes.
- AI Chatbots & Virtual Health Assistants – Provide 24/7 symptom analysis and health recommendations.
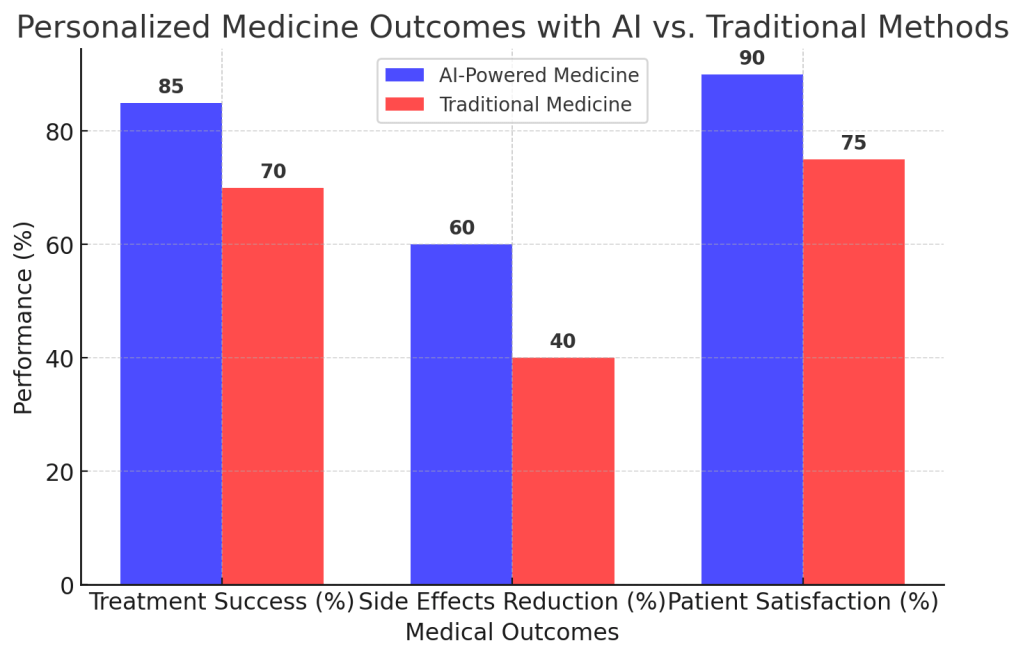
Example: IBM Watson Health has partnered with oncology centers to use AI for recommending personalized cancer treatment options, reducing trial-and-error in chemotherapy selection.
Graph: Personalized Medicine Outcomes with AI vs. Traditional Methods
Challenges & Ethical Considerations
Despite its potential, AI in healthcare faces key challenges:
- Data Privacy & Security – Ensuring compliance with HIPAA, GDPR, and other regulations when handling sensitive patient data.
- Model Transparency & Bias – AI models must be interpretable to avoid medical bias and ensure patient trust.
- Integration with Existing Systems – AI tools need to seamlessly work with electronic health records (EHRs) without disrupting clinical workflows.
Business Impact: AI in Healthcare Adoption
Hospitals, biotech firms, and health startups investing in AI are seeing significant benefits:
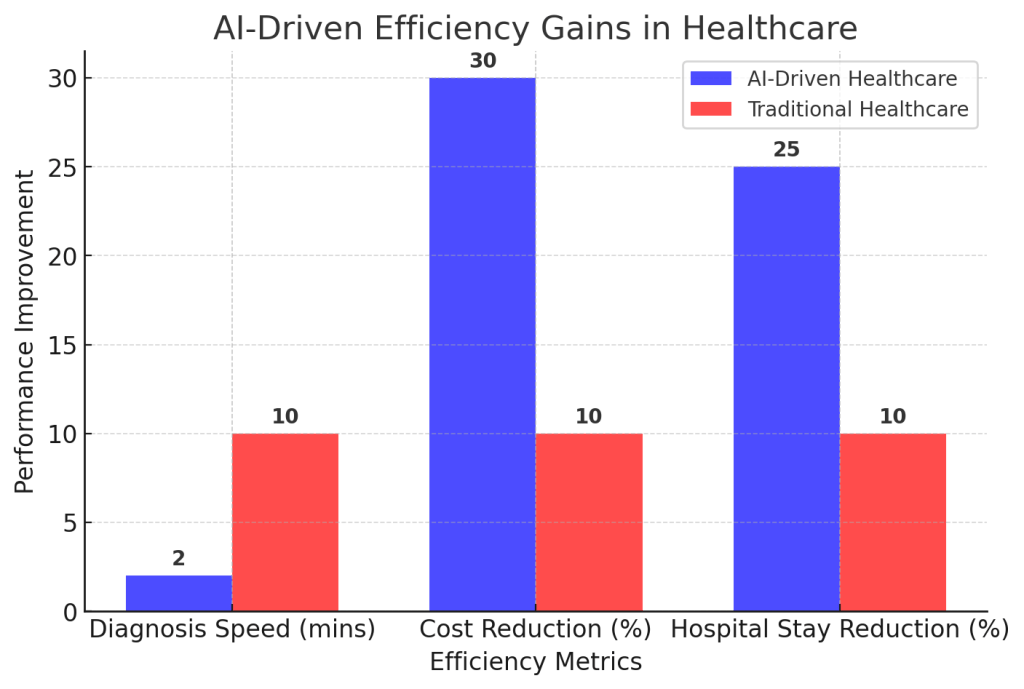
- Lower healthcare costs – AI streamlines administrative tasks, reducing operational expenses.
- Reduced diagnostic errors – AI-assisted radiology improves accuracy by 15-30%.
- Faster patient outcomes – AI-powered diagnostics shorten hospital stays by enabling earlier interventions.
Graph: AI-Driven Efficiency Gains in Healthcare
Looking Ahead: The Future of AI in Healthcare
The next wave of AI in healthcare is expected to bring:
- AI-Powered Drug Discovery – Speeding up pharmaceutical research and development.
- AI-Augmented Surgery – Robotics-assisted procedures with enhanced precision.
- Remote AI Diagnostics – Expanding healthcare access to underserved populations.
AI is not replacing doctors—it is empowering healthcare professionals with smarter tools for better patient outcomes.
Final Thoughts
AI in healthcare is already revolutionizing diagnostics, risk prediction, and personalized medicine. As AI technologies continue to evolve, they will play an increasingly vital role in preventive care, clinical decision-making, and patient engagement.
